All we need to know about proastate enlargement
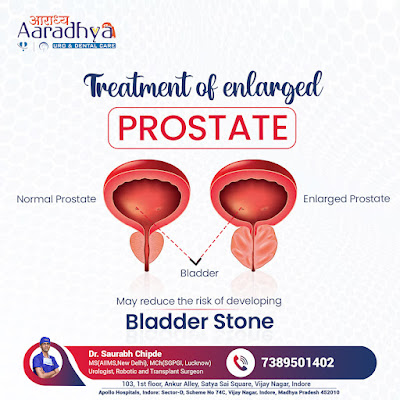
The prostate gland is a part of the reproductive system whose secretion supports sperm formation. This gland is located inside the abdomen just below the urinary bladder and on the topmost region of the urethra which drains urine from bladder to urethra. It is one among the three glands of a reproductive system whose secretion is alkaline and provides nutrition and lubrication for the maturation and motility of sperm. The prostate gland secretes fibrinolysin, zinc, prostate-specific antigen, a proteolytic enzyme, etc, and together with seminal vesicle forms the major fluid part of the seminal plasma and the semen also. Due to certain unknown regions the size of the prostate gland increases and affects the homeostasis of the body. If the size of the prostate increases it puts pressure on the bladder and the urethra too, through which urine is transported from the bladder out through the penis. In medical terms, this condition of enlarged prostate is called benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH.
Symptoms
Normally when a person has an urge to urinate, urine from the bladder moves to the urethra without any problem but when the prostate becomes enlarged it provides a barrier for urine to flow from the bladder to the urethra. In this condition, the patient suffers from multiple difficulties during urination such as:-
- Hasten to urinate.
- Periodic urination.
- Irregular urine flood.
- Sleeplessness due to frequent urination at night.
- Trouble in starting of urination.
- Drops of Blood in urine etc.
- Urine test.
- Blood test.
- Prostate-specific antigen test.
- Urine flow test etc.
- Transrectal ultrasound.
- Prostate biopsy.
- cystoscopy test etc.
- Doing meditation to control the stress full routine.
- Doing yoga and other pelvic floor exercises.
- Emptying bladder during urination.
- Avoiding taking fluid supplements at the night to avoid night urination.
- Avoiding smoking and alcohol.
- Consuming a high fiber diet and avoiding spicy and fatty meals.
- Discomfort or serious difficulty with urination.
- Kidney problems
- Drops of blood in the urine.
- Bladder stones
- TURP
- Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP)
- Laser surgery
- Urinary diversion etc.


Comments
Post a Comment